UF precollegiate center keeps teachers up to date on bioscience technologies
MOST OF THE TIME they are the teachers.
Not this time.
Dozens of high school teachers from across Florida returned to the classroom as part of an innovative University of Florida program to teach teachers the latest biomedical science and technologies, and to spark interest in bioscience careers among high schoolers.

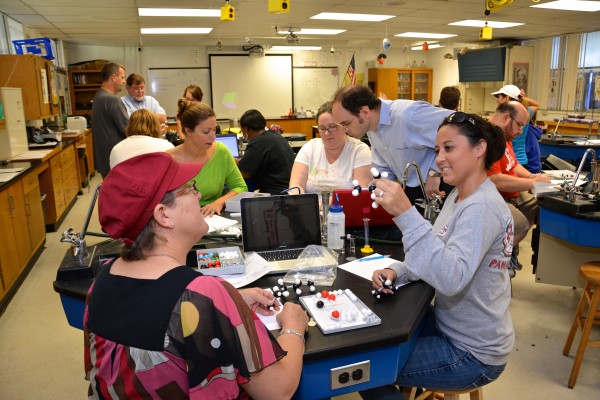
Kathy Savage participates in a laboratory exercise during the summer program with Houda Darwiche, a post doctoral fellow with the Center for Precollegiate Education and Training.

Secondary science teachers Wendy Vidor and Carlene Rogers get first-hand training in UF laboratories. Vidor, a UF doctoral student in horticulture science, teaches agricultural biotechnology and marine science at Matanzas High in Palm Coast; Rogers teaches AP biology and honors anatomy and physiology at Wekiva High in Apopka.
The idea: You can’t teach what you don’t know, and you know best when you learn firsthand.
“It is the best thing that ever happened to me as a teacher,” said Kathy Savage, a bioscience teacher at Oviedo High School in Oviedo who created a bioscience curriculum working with researchers on UF’s campus.
CPET is the University of Florida’s “umbrella” program and conduit for the transfer of science and technology to public school and community college teachers, students and the public-at-large.
“Our ultimate goal is to improve the teachers’ content knowledge,” said Julie Bokor, assistant director of CPET and a doctoral candidate in curriculum and instruction at UF’s College of Education.
Key Elements
Known as Biomedical Explorations: Bench to Bedside, the program includes four key elements.
- First, the high school teachers spend two weeks during the summer on UF’s campus where they conduct experiments and learn all manner of lab techniques and tools, such as applying technology to make copies of DNA, a method of diagnosing diseases, and identifying bacteria and viruses.
- Next, they develop lesson plans and incorporate these into their teaching during the school year.
- At year-end, they report their findings and disseminate the lessons so other teachers can use and help refine them.
- Finally, selected research fellows return to campus in subsequent summers and scatter across UF’s campus to work closely with professors in labs to more fully develop curricula.
To sum it up: UF professors transfer research and techniques to secondary teachers and these teachers translate this knowledge into lessons that students can best understand.
“It’s a professional learning cycle,” said Kent Crippen, an associate professor of STEM education in COE’s School of Teaching and Learning.
Applying Lessons Learned
Importantly, participating teachers aren’t set adrift after the initial summer camp: They receive continued support from CPET staff and professors.
A good example is Savage, who had taught chemistry for 17 years when she was tapped to create a bioscience program at her school. She was a fish out of water.
“The equipment and procedures and lab techniques weren’t around when I was in school,” Savage said. “It’s a little intimidating doing those kinds of experiments yourself when you have to teach your students.”
After participating in the inaugural cohort in 2010, she has since returned to campus for three weeks every summer to work closely with UF professors and post-doctorate scholars in UF labs. They have helped her design lesson plans, taught her to use science equipment that had been gathering dust at her school, corresponded to answer her questions via email and even visited her classroom to help conduct experiments.
“You never feel afraid to try something new and jump in because you know someone has your back,” she said.
Another example: Orlando Edgewater High biology teacher Jessica Mahoney and fellow CPET alumna Jennifer Broo worked with UF Associate Professor of Entomology Daniel Hahn to create lessons on the interrelated concepts of climate change and evolution.
Students conducted experiments on live fruit flies provided by the university’s Department of Entomology to determine which strains were most vulnerable to climate change based on their recovery from a chill-induced coma.
In previous summers, these teachers teamed to develop two other curricula: one involving the cell cycle and cancer and another exploring the evolution of horses.
All told, 105 high school teachers who have participated in the program are now bringing their new skills to their own classrooms, including 22 in the 2015-2016 school year as part of a second phase of the program.
Second Phase
The UF Bench to Bedside program recently received a two-year $522,698 follow-up grant from the National Institutes of Health to expand the dissemination of the new high school science curricula.
Crippen, a co-principal investigator of this phase-two project, is helping to widely circulate the lessons by training teachers to use a powerful open-source portal funded by National Science Foundation. This online repository is part of the NSF Digital Library and allows instructors to submit, download, collaborate, and manage the copyright of lesson plans and other teaching resources they have created for the program.
CPET, which is housed in the Office of the Provost, has a long history of close collaboration with the College of Education. Education Associate Dean Tom Dana initiated a course offering for the Bench to Bedside program so teachers completing the work receive three hours of graduate credit. In another program, CPET is supporting Rose Pringle, associate professor of science education, and P.K. Yonge Developmental Research School Director Lynda Hayes on a $5 million National Science Foundation grant known as U-FUTuRES (University of Florida Unites Teachers to Reform Education in Science) to train middle school science teacher-leaders to transform science teaching and learning. CPET Director Mary Jo Koroly is co-principal investigator on the project to facilitate science enrichment activities on campus.
Sharing lessons – and the lessons learned – is a key element of all this professional development work.
“Ultimately, what we want is for our teachers to get regional, state and even national recognition so they can develop professionally,” Bokor said. “By moving to the next level they get to share this great research.”
Contacts
Source: Julie Bokor, CPET, 352-392-2310
Source: Kent Crippen, College of Education associate professor of STEM Education, 352-273-4222
Writer: Charles Boisseau, UF COE News & Communications, 352-392-4449