Posts
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
labellebrittany
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
labellebrittany2018-05-10 17:22:132019-08-06 13:54:48EduGators awarded editor posts at national journals
labellebrittany
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
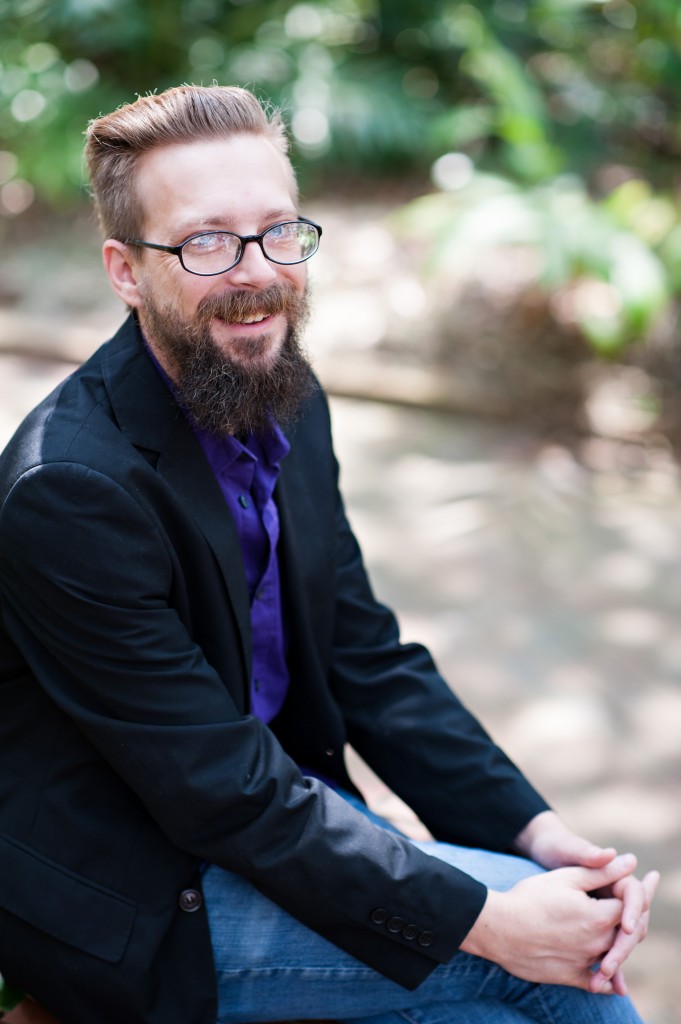
labellebrittany2018-04-12 21:00:582019-08-06 13:58:31AERA honors UF Special Ed professor for impactful research
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2018/02/patterson.jpg
400
600
labellebrittany
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
labellebrittany2018-02-26 12:30:322019-09-17 15:15:03Novelist's $3M gift could mean happy ending for struggling readers
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
labellebrittany
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
labellebrittany2018-02-09 00:01:272019-08-06 14:01:00UF scholar doubles up on national honors for advancing learning disabilities field
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2016-06-27 09:14:252016-08-15 13:19:25UF awarded $10M to personalize online math learning
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2015-04-01 12:50:342015-04-01 15:24:43Special Ed’s Gage recognized as rising international scholar in emerging field
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2015-03-02 12:16:392015-03-02 12:15:17Special ed. colleagues share national honor for teacher education achievements
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2015-02-23 14:27:032015-03-02 12:17:57Folio Weekly -- Why do some Florida schools still practice paddling?
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2014-12-11 14:10:202014-12-11 14:10:20In Memoriam: Cecil D. Mercer, Ph.D., special education 'giant'
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2014-10-07 14:15:572019-08-06 13:31:17Five more states join UF center's $25 million effort to transform special education teaching
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2014-06-04 13:07:122014-06-04 13:09:51UF teacher prep program is first in state accredited by international dyslexia group
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2014-04-01 06:30:442014-04-03 14:07:17Florida among 5 states partnering with new UF center to transform teaching of students with disabilities
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2014-03-21 06:00:132014-03-20 14:42:04International group honors Special Ed researcher for 2nd straight year
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
0
0
https://education.ufl.edu/news/files/2019/07/News-1-300x65.png
2013-05-23 17:02:362013-05-23 17:07:03UF special ed professor honored as distinguished alum
Scroll to top